Can a body corporate become a partner of an LLP?
Introduction
The question regarding the eligibility of a body corporate (both Indian as well as non-Indian) acting as a partner in a Limited Liability Partnership (hereinafter, “LLP”) has eluded Indian corporate law scholars and practitioners alike. While the short answer to this question is a “yes”, we need to look into the basics of LLP registration and its concerning laws to better understand the structure of LLPs and how they operate. In furtherance of the same, this article has been divided into three broad parts: the first part looks at Limited Liability Partnerships and the law surrounding them in India. It also addresses some of the most important definitions under the Act. The second part looks at the question of body corporates acting as partners in LLPs, and the various requirements that need to be fulfilled in doing so. The third part looks at the appointment and nomination of designated partners in cases where body corporates act as partners in LLPs. The last part concludes this article.
Limited Liability Partnerships
Some of the important definitions and provisions under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 (hereinafter, “the Act”) are as follows: As per section 2(n) of the Act, 2008, a “limited liability partnership” means a partnership formed and registered under the act. On the other hand, a “body corporate” includes a company incorporated outside India, but does not include
(i) a co-operative society registered under any law relating to co-operative societies; and
(ii) any other body corporate (not being a company as defined in this Act), which the Central Government may, by notification, specify in this behalf.
Further, Section 3 states that an LLP is a body corporate formed and incorporated under the Act and possesses a separate legal entity from that of its partners.
Thus, a collective reading of the aforementioned provisions suggests that an LLP is a body corporate which has been formed and incorporated under the Act and has a separate legal entity from that of its partners. Further, it also has a perpetual succession, which remains unaffected by any change in its partners. Thus, the rights, the liabilities, and the existence of an LLP remain unaffected by the same.
Body Corporates as Partners in a Limited Liability Partnership
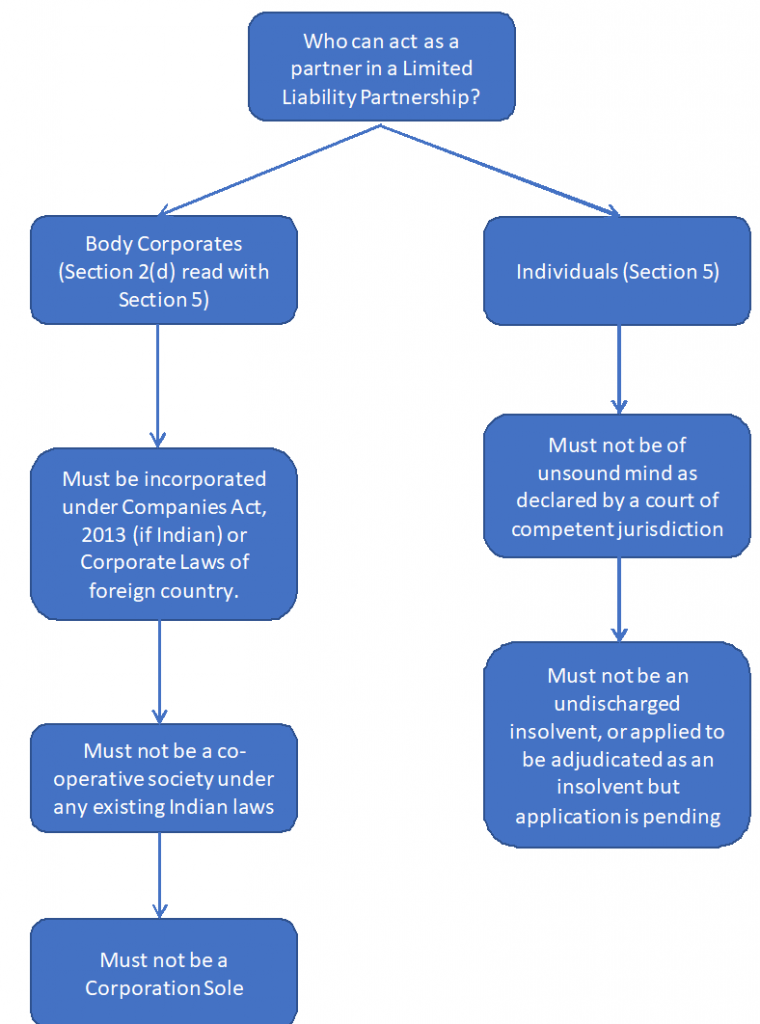
Before addressing the most important question, it is important to look at one of the provisions of the Limited Liability Partnership Act: Section 5. It is clarified that “any individual or body corporate may be a partner in a limited liability partnership”. Reading the definition of “body corporate” from Section 2(d) makes it clear that a company registered under the Indian Companies Act (Companies Act, 2013) or incorporated outside India can be a partner in a Limited Liability Partnership.
Given the immense amount of importance attached with this question, it has also been addressed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs in its “FAQs on Partners and Designated Partners” as a part of the LLP Basic Concepts section. Even the FAQs by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs make it clear that a body corporate can act as a partner in an LLP.
Thus, the three requirements that need to be fulfilled by a company willing to act as a partner are
(i)(a) if it is an Indian company, it must be incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013, and (i)(b) if it is a foreign company, it must be duly incorporated under the corporate laws of that particular country,
(ii) it must not be a co-operative society registered under any of the laws currently in force in India, and
(iii) it must not be a corporate sole, i.e. a legal entity consisting of a sole incorporated office, that has been occupied by just one natural person.
At this juncture, while it is clear that a body corporate can act as a partner in an LLP, it raises the pertinent question of designated partners in LLPs where one or more partners is a body corporate, since the Act requires the designated partners to be individuals and not body corporates. The next part aims to address this very question.
Designated Partners and LLPs with body corporates as partners
An important requirement for the functioning of an LLP under the Act is that of “designated partners”. As per Act, every LLP must have at least two designated partners who are individuals, and at least one of them must be a resident of India. Designated partners as per the Act are responsible for the “doing of all acts, matters and things as are required to be done by the LLP in respect of compliance of the provisions” under the Act, including filing of any document, return, or such statement as is required under the provisions of the Act.
Further, designated partners are also held liable if any of the regulatory, legal compliances or even the post registration compliance for LLP are not fulfilled. Appointment of designated partners becomes an issue when one or more partners in an LLP are body corporates. This is primarily problematic because designated partners must be two individuals, one of whom must be a resident of India (which, as per the act, means that the person has resided in India for not less than 182 days in the preceding year).
To remedy this situation, the Act through other section suggests that in cases where all the partners in the LLP are body corporates, or in which one or more partners is an individual and a body corporate, the body corporate must nominate people to act as designated partners unless two individuals who are partners of such LLP are available to act as designated partners. Similar to the previous part, even this question has been addressed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs in its “FAQs on Partners and Designated Partners” as a part of the LLP Basic Concepts section. Even there, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs reaffirms this position.
Conclusion
To conclude, this article has tried to address the question of body corporates acting as partners in LLPs. To that end, the article has been divided into three parts. The first part analyzes the law surrounding Limited Liability Partnerships in India, and concludes that LLPs are a separate legal personality from their partners, and have a perpetual existence independent of their partners. The second part looks at body corporates as partners in an LLP, and concludes that body corporates can act as partners in an LLP, provided that they have been incorporated in accordance with the corporate laws of the country, are not co-operative societies, and are not corporate soles.
The third and final part looks at the appointment of designated partners in cases where body corporates are partners in LLPs and concludes that in case where all partners are body corporates, such body corporates need to nominate people who can act as designated partners. In case where some of the partners are body corporates and rests are individuals, two partners from within the individuals (one of whom is resident in India) must be appointed as the designated partners with their due consent.

Pranav Mehta
Our guest editor, Pranav Mehta, is a final year student at NLSIU Bangalore. He has served on the editorial boards of the Indian Journal of Law and Technology (IJLT) and the Indian Journal of International Economic Law (IJIEL). He has also cleared the CFA Level 1 exam.
