Common Mistakes in GST Filings for SMEs
Goods and Services Tax (GST) has transformed the way businesses operate in many countries, including India. For small and medium enterprises (SMEs), navigating the complexities of GST filing can be daunting. Many SMEs make common mistakes that can lead to financial penalties as well as compliance issues. This article explores these common GST filing mistakes, offering insights on how to avoid them.
Understanding GST Filing
GST filing is a mandatory process for businesses registered under the Goods and Services Tax regime. It involves submitting various forms, such as GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B, to report sales, purchases, and tax liabilities. Proper GST return filing is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring that businesses do not face unnecessary penalties.
Common GST Filing Mistakes
Here are some GST filing errors that SMEs should be aware of when GST return Filing:
1. Manual Data Entry Errors
One of the most frequent GST filing mistakes is manual data entry errors. These can include incorrect invoice numbers, wrong amounts, or misformatted dates. Such errors can lead to discrepancies in the filed returns, resulting in penalties or audits. To mitigate this risk, businesses should implement robust accounting software that minimizes manual input and also automates data entry.
2. Incorrect Tax Slab Application
One of the common GST filing Mistakes is applying incorrect tax slabs to goods and services. The GST regime has multiple tax slabs (0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%), and misclassifying products can lead to significant errors in tax calculation. SMEs must ensure they understand the applicable tax rates for their products by regularly reviewing the GST guidelines.
3. Non-filing of NIL Returns
Many SMEs overlook the requirement to file NIL returns when there are no transactions during a tax period. Failing to file these returns can result in penalties and complications with future filings. It is essential for businesses to remain vigilant about their filing obligations, even during inactive periods.
4. Confusing Zero-Rated Supply with Nil-Rated Supply
Understanding the difference between zero-rated and nil-rated supplies is crucial for accurate GST filing. Zero-rated supplies refer to exports or supplies made to Special Economic Zones (SEZs) that are taxed at 0%, while nil-rated supplies are those exempt from GST altogether. Misclassification can lead to incorrect reporting, which is one of the most common GST filing Mistakes.
5. Mismatched Returns
SMEs often face issues when there is a mismatch between GSTR-1 (outward supplies), GSTR-3B (summary return), and annual returns (GSTR-9). The GST system requires these returns to match up accurately; discrepancies can trigger notices from tax authorities. Regular reconciliation of these returns before submission is vital to avoid mismatches.
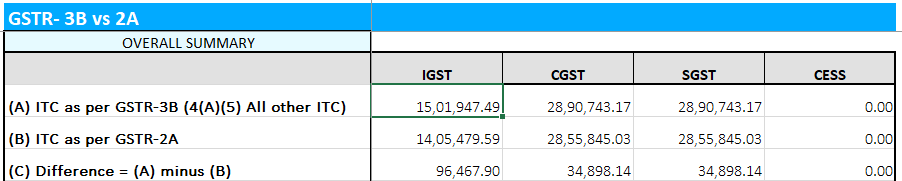
6. Ignoring Input Tax Credit (ITC) Reversals
Claiming Input Tax Credit (ITC) incorrectly or failing to reverse ITC when necessary is another common error. If a business claims ITC on purchases that do not qualify or fails to reverse it when goods are returned, it could face penalties during audits. SMEs should maintain meticulous records of all transactions and understand the conditions under which ITC can be claimed or reversed.
7. Not Keeping Adequate Records
Proper documentation is essential for successful GST filing. Many SMEs fail to maintain adequate records of sales invoices, purchase invoices, and other relevant documents, which can complicate the filing process and lead to errors. Implementing a systematic record-keeping process ensures that all necessary documents are available during filing periods.
8. Failing to Update Registration Details
SMEs must keep their GST registration details updated, including changes in business structure or address. Neglecting to update this information can result in complications during filing or even penalties for non-compliance. Regularly reviewing registration details ensures that businesses remain compliant with current regulations.
9. Not Understanding Filing Deadlines
Each type of GST return has specific deadlines for submission, which SMEs often overlook. Missing these deadlines can result in late fees as well as interest charges on unpaid taxes. It is crucial for businesses to stay informed about due dates and also set reminders well in advance of these deadlines.
10. Lack of Professional Guidance
Many SMEs attempt to handle their GST filings independently without adequate knowledge of the complexities involved, leading to major GST filing mistakes that could have been avoided with professional assistance. Engaging with a qualified accountant or tax professional can provide valuable insights into proper compliance practices and also help navigate the intricacies of the GST system.
How to File GSTR-1 Correctly
Knowing how to file gstr1 in gst portal accurately is critical as it outlines outward supplies made by a business during a tax period. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to file GSTR-1 effectively:
- Log into the GST Portal: Firstly, use your credentials to access your account.
- Select ‘Returns’: Navigate to the ‘Returns’ section on the dashboard.
- Choose GSTR-1: Select GSTR-1 from the list of available forms.
- Fill Out Details: Enter all required details regarding outward supplies accurately.
- Review Entries: Double-check all entries for accuracy before submission.
- Submit: Once confirmed, submit the form electronically through the portal.
- Download Acknowledgment: Finally, after submission, download the acknowledgement receipt for your records.
Conclusion
GST filing is an essential aspect of running an SME that requires careful attention to detail as well as adherence to regulations. By being aware of common GST filing mistakes such as manual data entry errors, incorrect application of tax slabs, non-filing of NIL returns, confusion between zero-rated and nil-rated supplies, mismatched returns, improper handling of ITC reversals, inadequate record-keeping, failure to update registration details, missing deadlines, and lack of professional guidance, SMEs can significantly reduce their risk of compliance issues.
Implementing best practices in bookkeeping and seeking professional assistance when necessary will help ensure accurate GST filing and foster smoother operations within an SME’s financial management framework.

Monjima Ghosh
Monjima is a lawyer and a professional content writer at LegalWiz.in. She has a keen interest in Legal technology & Legal design, and believes that content makes the world go round.
